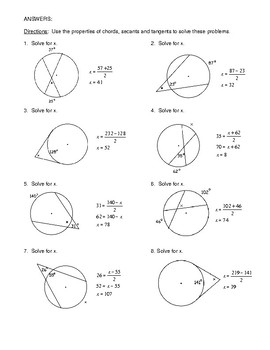
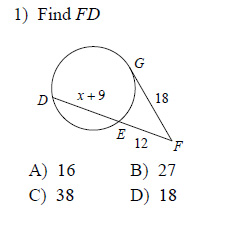
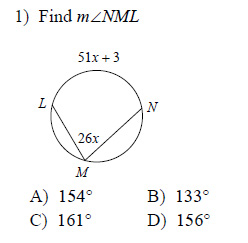
Tangents And Secants Of Circles Worksheet. Your students will use these worksheets to learn how to calculate line lengths inside and outside of circles by using tangents. A straight line which cuts curve into two or more parts is known as a secant.

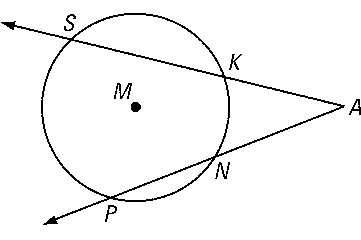
It is a straight line that meets the circle at any point, and we will say this process the point of tangency.
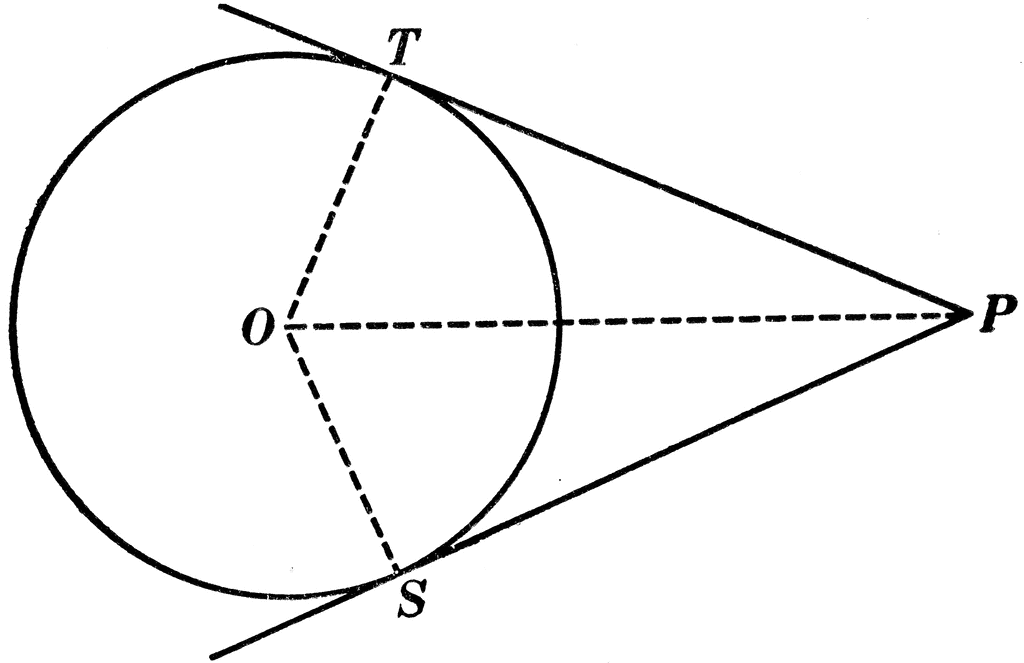
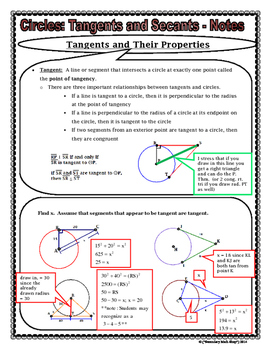
Include the relationship between central, inscribed, and circumscribed angles; inscribed angles on a diameter are right angles; the radius of a circle is perpendicular to the tangent where the radius intersects the circle.
Secant passes through the center of the circle. Segments drawn within, through, or tangent to a circle create angles which we will now define and measure. A tangent line just touches a curve at a point, matching the curve's slope there. (From the Latin tangens "touching", like in the word "tangible".) Circles: Chords, Secants & Tangents.